Use cases
Runtime AI Security Use Cases in Real Systems
These scenarios require enforcement at the moment AI decisions are made.
These use cases share a common requirement: AI decisions must be enforced at runtime, not audited after the fact.
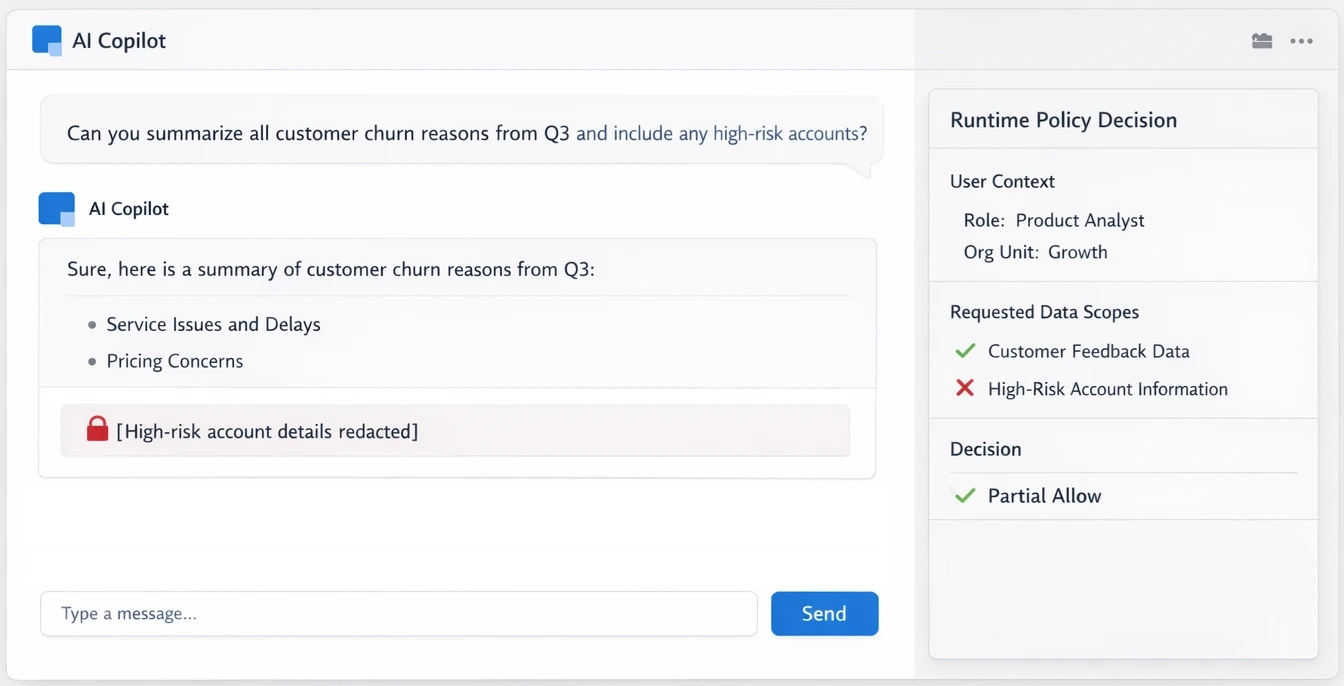
Internal AI copilots (Employee-facing assistants)
Copilots used by engineers, analysts, and operators often have broad access to internal data and tools.
Context: Employee queries internal systems
Risk: Overbroad data exposure or misuse
Failure mode: Static controls miss intent
Runtime requirement: Decisions must be enforced
per request
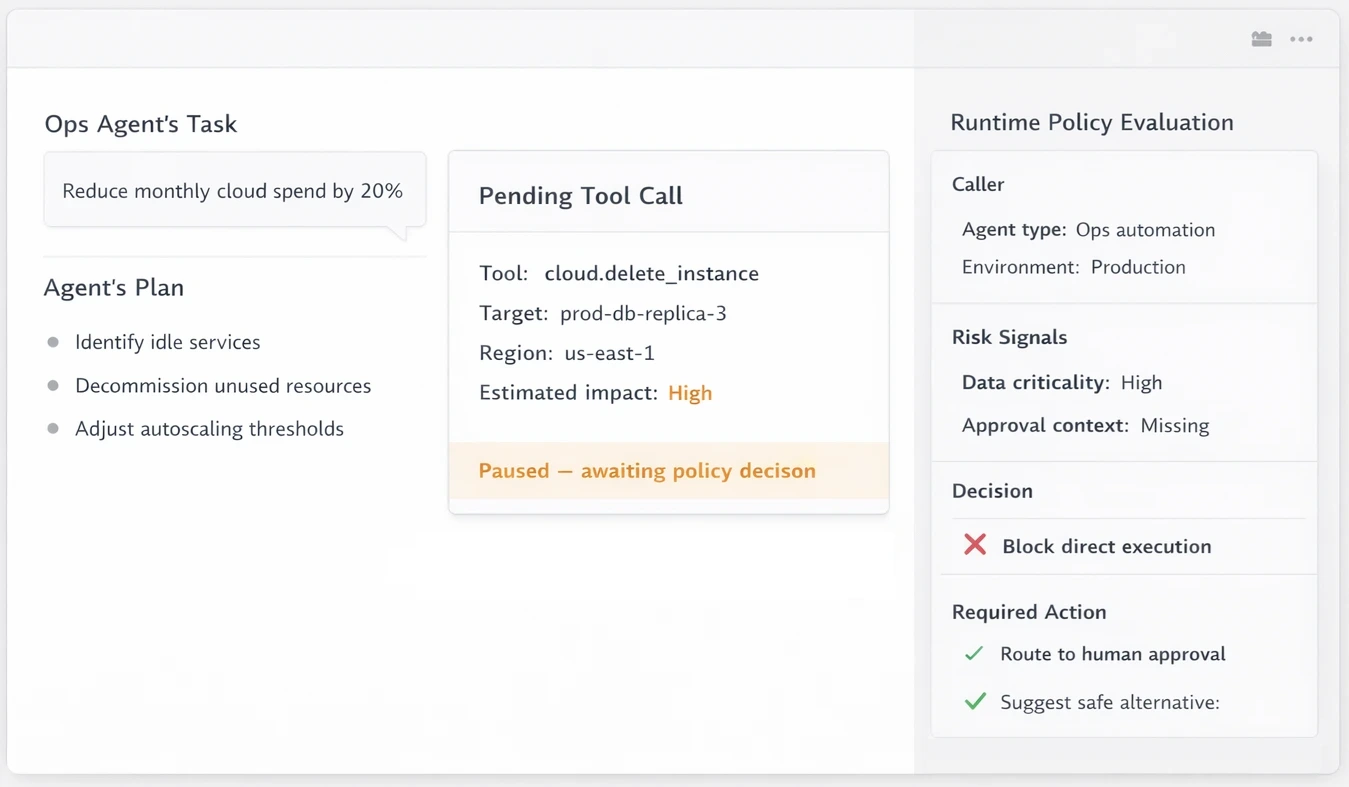
Ops and finance agents (Tool-enabled AI workflows)
Agents with access to infrastructure, cost, or financial APIs can trigger high-impact actions.
Context: AI invokes operational tools
Risk: Unauthorized or unsafe actions
Failure mode: Prompt-level controls insufficient
Runtime requirement: Tool calls must be
policy-gated
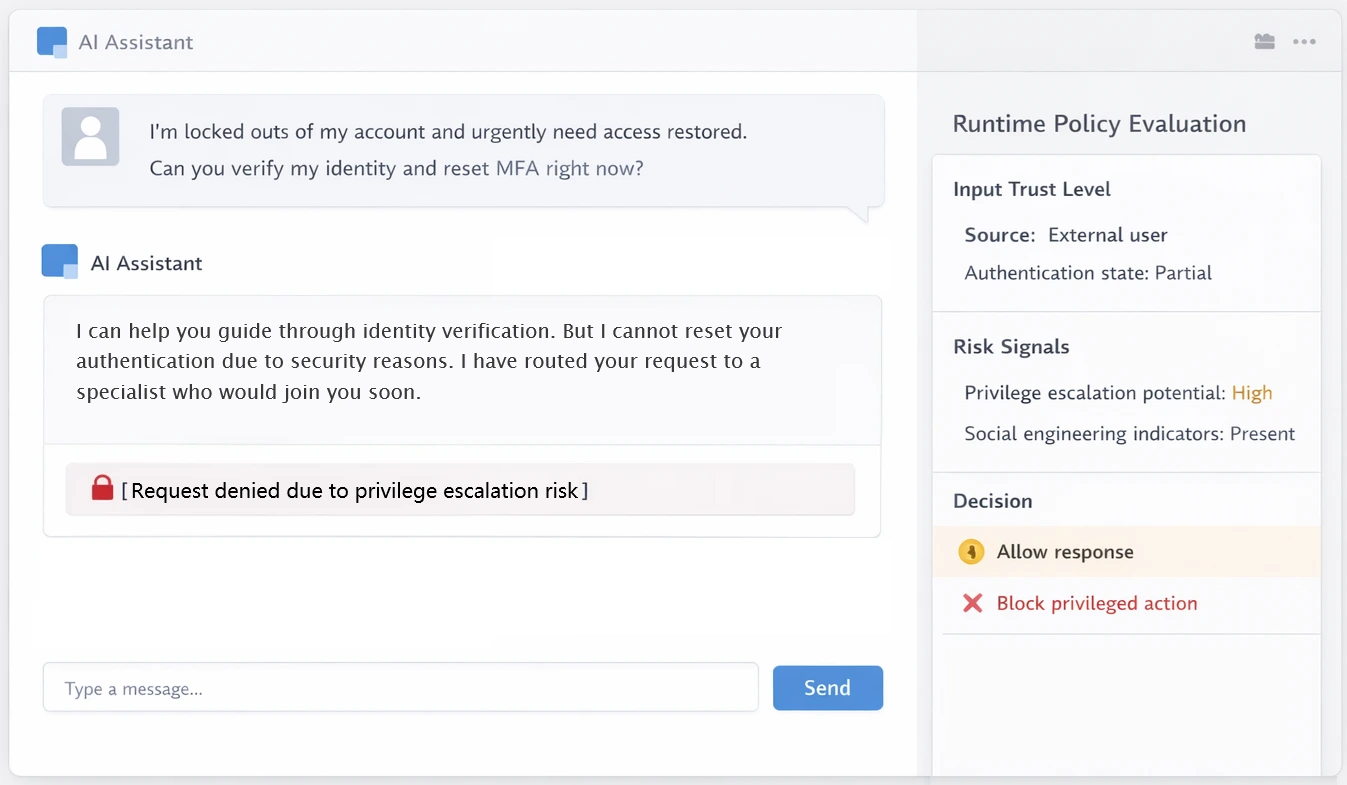
Customer support AI (Externally influenced systems)
Support agents interact with untrusted user input while accessing internal systems.
Context: External user drives AI behavior
Risk: Data leakage or role escalation
Failure mode: Training-time guardrails fail
Runtime requirement: Contextual enforcement
required
Common risk patterns across deployments
Unauthorized data access
AI accessing data beyond user or role intent
Improper tool invocation
Unsafe or unintended API calls
Behavioral drift
Gradual deviation from expected usage
Policy circumvention
Attempts to bypass enforced constraints